Book Appointment Now

Dental Abscess – Your Complete Guide with Images, Medications, and Modern Treatments
A dental abscess is one of the most painful and bothersome oral health problems, affecting millions each year. If not treated promptly, what begins as a small swelling in the gum can escalate into a serious infection threatening the bone and bloodstream.
In this comprehensive medical guide, we’ll explore dental abscesses from all angles:
Types – Causes – Images – Treatments – Medications – FAQs – and finally, Prevention.
Table of Contents
What Is a Dental Abscess?
A dental abscess is a buildup of pus caused by a bacterial infection inside the tooth or in the surrounding gum or bone. This infection develops when bacteria enter the root or internal canals of the tooth due to deep decay, trauma, or unsterile procedures.
Difference Between a Tooth Abscess and a Molar Abscess
- Tooth Abscess: Involves any tooth, whether front or back.
- Molar Abscess: Typically affects back molars and may be deeper and more painful.
Types of Dental Abscesses
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Internal Abscess | Infection starts inside the tooth due to decay or nerve damage |
| Sub-molar Abscess | Affects the root below the molar, often invisible to the naked eye |
| Gum Abscess | Appears as a pus-filled bump on the gums |
| External Surface Abscess | Appears as swelling in the cheek or below the jaw |
Dental Abscess in Pictures: What Does It Look Like?
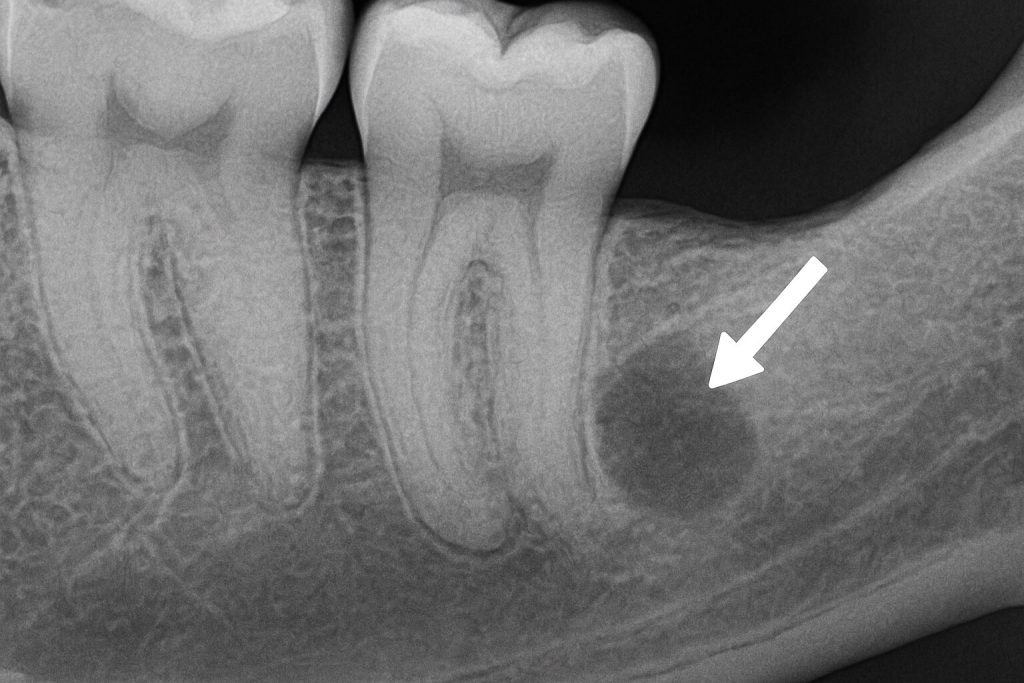
1. Internal Abscess (Periapical Abscess)
Originates from within the tooth, specifically in the dental pulp which contains nerves and blood vessels.
Often caused by deep decay reaching the nerve, allowing bacteria to multiply and form pus.
Common symptoms: Deep pain, pressure sensitivity, pain when lying down.
2. Sub-Molar Abscess
Forms below the tooth root and often goes unnoticed without an X-ray.
This type can become chronic, causing pain when biting or pressure is applied.
Important Note: Often linked to incomplete root canal treatment.
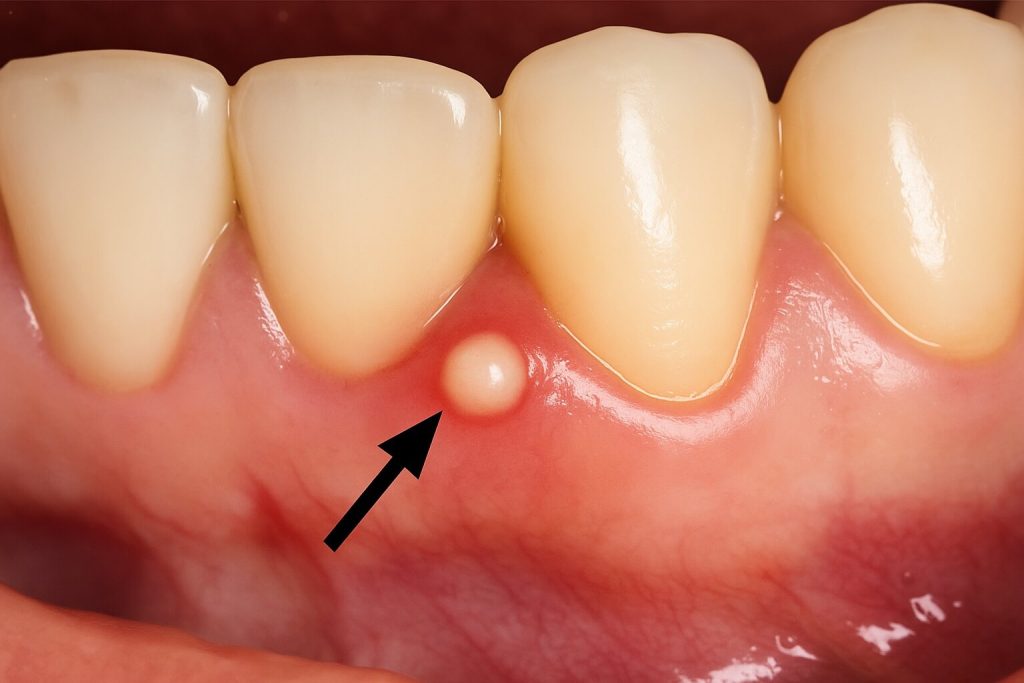
3. Gum Abscess (Periodontal Abscess)
Caused by severe gum disease or advanced periodontitis.
Bacteria enter through gum pockets (space between tooth and gum), forming an external pus sac.
Signs: Swollen gum surface, red or purplish color, localized pain.
4. Abscess from Orthodontic Devices or Fillings
Sometimes, braces or poorly fitted fillings irritate the gums or trap bacteria.
High or leaky fillings can create an environment that encourages abscess formation.
Causes of Dental Abscess
- Untreated deep tooth decay
- Cracked or damaged tooth allowing bacterial entry
- Old or loose dental work
- Advanced gum disease
- Poor oral hygiene
Explore all our specialized services, from abscess treatments to advanced surgical care.
Symptoms of a Dental Abscess
- Sharp, persistent pain (often worse at night)
- Swelling in the cheek or gums
- Neck or jaw swelling
- Difficulty eating or speaking
- Bitter taste or pus in the mouth
- Fever or fatigue
Suffering from dental pain or swelling?
Don’t delay – Book your appointment now for pain relief and root cause treatment.
⚠️ Warning: If you experience difficulty breathing or swallowing, seek emergency care immediately.
Diagnosis of Dental Abscess
1. Clinical Examination
Dentist checks for visible swelling or pus discharge.
2. X-rays
Reveals depth and location of the abscess.
3. Pus Culture (Rare)
Used to identify bacterial type in advanced cases.
Best Antibiotic for Dental Abscess
| Antibiotic | Dosage | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 500 mg every 8 hours | First choice in most cases |
| Metronidazole | 400 mg every 8 hours | Effective against anaerobic bacteria |
| Augmentin | 1 g every 12 hours | For more extensive infections |
| Cefixime | Dose by weight (syrup) | For children |
💡 Tip: Never use antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription.
Dental Abscess Treatment Step by Step
1. Does the Abscess Always Need Draining?
Not always. Sometimes it drains naturally or responds to antibiotics.
But if swelling is large, pain is severe, or signs of systemic infection appear, the dentist may perform a small surgical incision to drain the pus.
Final decision depends on clinical evaluation and imaging results.
2. Eliminate the Source of Infection
- If the tooth is salvageable → Root canal (nerve treatment)
- If severely damaged → Extraction
3. Appropriate Antibiotics
Depends on bacterial type and patient’s health status. Usually includes Amoxicillin, Augmentin, or Metronidazole.
Home Remedies for Molar Abscess (Temporary Relief)
- Rinse with warm saltwater three times daily
- Cold compress to reduce swelling
- Safe painkillers like Paracetamol
- Avoid chewing on the affected side
🚫 These only offer temporary relief. A dentist visit is essential.
Treating Dental Abscess in Children
- Safe antibiotics (like Cefixime or Amoxicillin syrup)
- Gentle cleaning if possible
- Filling or extraction based on dentist’s evaluation
Teaching children good oral hygiene early is key to prevention.
Complications of Dental Abscess
- Bone damage around the tooth
- Infection spreading to sinuses
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Sepsis (blood poisoning)
- Heart problems in valve patients
Preventing Dental Abscess
Simple steps to avoid pain and risk:
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Use dental floss every day
- Limit sweets and fizzy drinks
- Visit your dentist every 6 months
- Treat cavities promptly before they worsen
Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Abscess
Does a dental abscess go away on its own?
No, and neglecting it can lead to serious complications.
How long does dental abscess treatment take?
Typically 5 to 10 days depending on severity.
Can an abscess burst on its own?
Yes, but that doesn’t mean it’s healed. Further treatment is needed.
What’s the difference between a gum abscess and a molar abscess?
Gum abscess is superficial, caused by gum problems.
Molar abscess is deeper, affecting the root.
Is an antibiotic alone enough?
Sometimes, yes. But many cases need minor surgical intervention too.
Does a dental abscess cause bad breath?
Yes, especially if pus drains into the mouth.
Conclusion
A dental abscess is not to be taken lightly. It signals something seriously wrong inside your mouth that needs prompt attention to avoid pain and complications.
The good news? Most abscesses are easily treatable if caught early.
Our final advice: Don’t wait for the pain to get worse. Start protecting your teeth today.







